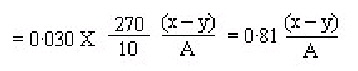S.I. No. 44/1950 - Standard Specification (Asbestos-Cement Slates and Sheets) Order, 1950.
S.I. No. 44 of 1950. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
STANDARD SPECIFICATION (ASBESTOS-CEMENT SLATES AND SHEETS) ORDER, 1950. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
I, DANIEL MORRIRSSEY, Minister for Industry and Commerce, in exercise of the power conferred on me by subsection (3) of section 20 of the Industrial Research and Standards Act, 1946 (No. 25 of 1946), hereby order as follows : 1. This Order may be cited as the Standard Specification (Asbestos-Cement Slates and Sheets) Order, 1950. 2.—(1) The specification set forth in Part II of the Schedule to this Order is hereby declared to be the standard specification for the commodity described in Part I of the said Schedule. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(2) The said standard specification may be cited as Irish Standard 7 : 1950. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SCHEDULE. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PART I. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ASBESTOS-CEMENT SLATES AND SHEETS. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PART II. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SPECIFICATION. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In this specification, the letters B.S., when followed by two sets of numbers, refer to the British Standard of which the first is the serial number and the second is the year of its publication by the British Standards Institution. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SECTION I : | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
GENERAL. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SCOPE. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1. This specification refers only to asbestos-cement slates and unreinforced flat and corrugated sheets, both straight and curved. It does not apply to reinforced sheets. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
COMPOSITION. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2. The product shall be composed of an inert aggregate consisting of clean asbestos fibre cemented together by an inorganic cement consisting essentially of hydrated calcium silicates and aluminates. Colouring matter may be added if desired. Only inorganic colouring matter and/or carbon black may be added to the composition. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
COLOURING MATTER. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3. Pigments that are embodied in the asbestos-cement for colouring purposes shall be of permanent colour and shall conform to B.S. 1014 : 1942, Pigments for Colouring Cement, Magnesium Oxy-chloride and Concrete. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FREEDOM FROM DEFECTS. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4. The finished products when delivered shall be free from visible defects and shall have been manufactured for at least four weeks. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
INSPECTION. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5. The purchaser, or his representative, shall have access at all reasonable times to the manufacturer's stock area for the purpose of selecting from his consignment the slates or sheets to be tested. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MANUFACTURER'S CERTIFICATE. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6. The manufacturer, upon request, shall furnish the purchaser, or his representative, with a certificate that the finished products comply with this specification. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TESTING. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7. The manufacturer shall supply labour and appliances at his own expense for such tests as may be carried out on his premises in accordance with this specification. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
When tests are required to be made in the presence of the purchaser, or his representative, this shall be stated in the enquiry and order, and the cost of the finished products necessary for such tests shall be borne as follows : | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(a) by the manufacturer in the event of the results showing that the material does not comply with the specification. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(b) by the purchaser in the event of the results showing that the material complies with the specification. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All tests shall be made before despatch and all products shall have been manufactured for at least four weeks before the date of test. In the case of materials covered by Section III of this specification the date of manufacture shall be impressed thereon at the time of manufacture. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ADDITIONAL TESTS BEFORE REJECTION. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8. Should any of the tests fail to comply with the requirements laid down, two repeat tests shall be made of the test under which failure occurred. If the results obtained from both the repeat tests are satisfactory the material represented shall be accepted. Should either of the repeat tests fail, the material represented shall be rejected. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SECTION II. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SLATES AND FLAT SHEETS. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MANUFACTURE. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
9.—(a) Slates. Slates shall be consolidated under pressure and shall be smooth on both sides. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(b) Flat sheets. Flat sheets shall be rectangular, have a plane surface on one side, and shall have neatly trimmed edges. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DIMENSIONS AND TOLERANCES. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
10.—(a) Dimensions of slates and flat sheets. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The slates and flat sheets shall conform to the dimensions given in Tables 1 and 2. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(b)—Tolerances. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(i) Slates. The permissible tolerance on the thickness of slates shall be as given in Table 1. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(ii) Flat Sheets. The length and breadth of flat sheets shall not vary from the appropriate values given in Table 2 by more than plus or minus 0·25 per cent. The mean thickness of the sheets shall not differ from the nominal thickness specified in Table 2 by more than plus or minus 10 per cent. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TRANSVERSE TEST.* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
11.—(a) Average breaking load. The average breaking load of six square specimens measuring 10 in. by 10 in. cut from slates or flat sheets, when tested wet over a 9 in. span in the manner described in Appendix A, shall be not less than the values given in the following table :— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
* This method of test is not applicable to curved sheets. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
BREAKING LOAD IN POUNDS. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Note.—The fibres run parallel or at right angles to the edges of the slate or sheet. In the case of slates from which a 10 in. by 10 in. specimen cannot be obtained, a specimen 10 in. by 5 in. shall be used and tested with the same 9 in. span. (See Appendix A.) The breaking load obtained shall be not less than one-half the value for the appropriate fibre direction given in the table above for the 10 in. by 10 in. specimen of the same thickness. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(b) Uniformity. If the breaking strength of any specimen is less than 70 per cent. of the average breaking strength of the six specimens tested, a further six specimens shall be tested and the results combined with five of the previous results, the lowest result having been eliminated. The breaking strength of any one of the eleven specimens shall be not less than 70 per cent. of the average breaking strength of the eleven specimens. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
WATER ABSORPTION TEST. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
12. The average amount of water absorbed when specimens are tested in the manner described in Appendix C, shall not exceed 20 per cent. of the dry weight in the case of slates, and 28 per cent. of the dry weight in the case of flat sheets. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TEST FOR RESISTANCE TO ACIDIC WATERS. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
13. The average amount of acetic acid consumed when specimens are tested in the manner described in Appendix D, shall not exceed 0·115 g. per sq. cm. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SECTION III. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CORRUGATED SHEETS. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
GENERAL. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
14. Corrugated sheets shall be classified according to the size and form of the corrugations as follows :— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The sheets shall be corrugated in a true and regular manner. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DIMENSIONS AND TOLERANCES. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
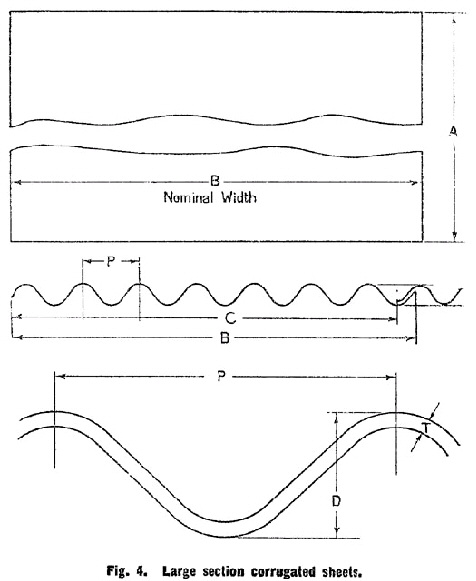
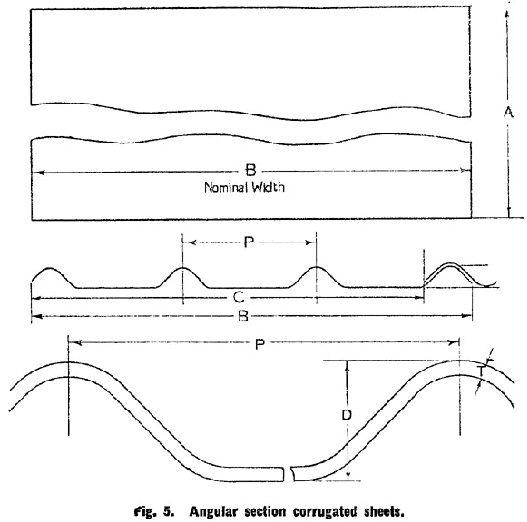
15.—(a) Dimensions. The corrugated sheets shall, within the limits of tolerance specified in Clause 15 (b), conform to the linear dimensions given in Tables 3, 4 and 5. The thickness* shall be not less than that specified in those tables. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
* For the purpose of measuring the thickness it is recommended that a sliding gauge having a blade not more than 1 in. long and approximately 1/8 in. thick be used. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(b) Tolerances. Corrugated sheets shall not vary from the dimensions for length and width specified in Tables 3, 4 and 5 by more than plus or minus 0·25 per cent. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TRANSVERSE TEST.† | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
† This method of test is not applicable to curved sheets. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
16.—(a) Average breaking load. When tested wet in the manner described in Appendix B, the average breaking load of three specimens shall be not less than the values given in the following table :— | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(b) Uniformity. If the breaking strength of a specimen is less than 70 per cent. of the average breaking strength of the three specimens tested, a further three specimens shall be tested and the results combined with two of the previous results, the lowest result having been eliminated. The lowest breaking strength of any one of the five specimens shall be not less than 70 per cent. of the average breaking strength of the five specimens. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
WATER ABSORPTION TEST. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
17. The average amount of water absorbed when specimens are tested in the manner described in Appendix C, shall not exceed 28 per cent. of the dry weight. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TEST FOR RESISTANCE TO ACIDIC WATERS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
13. The average amount of acetic acid consumed when specimens are tested in the manner described in Appendix D, shall not exceed 0·115 g. per sq. cm. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
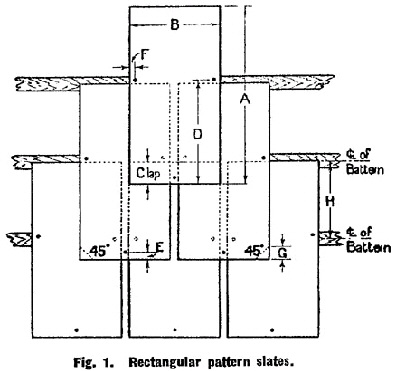
TABLE 1. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DIMENSIONS OF REINFORCED PATTERN SLATES. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See Fig. 1. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
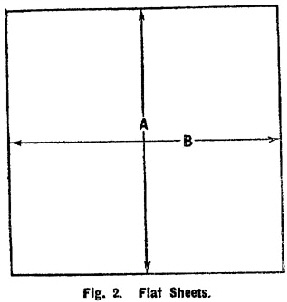
TABLE 2. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DIMENSIONS OF FLAT SHEETS. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See Fig. 2. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
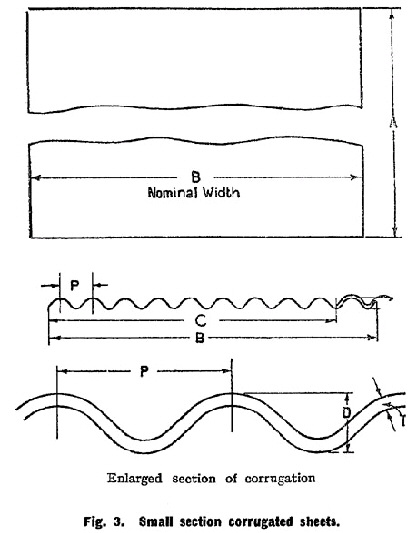
TABLE 3. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DIMENSIONS OF SMALL SECTION CORRUGATED SHEETS. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See Fig. 3. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TABLE 4. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DIMENSIONS OF LARGE SECTION CORRUGATED SHEETS. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See Fig. 4. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TABLE 5. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DIMENSIONS OF ANGULAR SECTION CORRUGATED SHEETS. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See Fig. 5. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
APPENDIX A.* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
*This method of test is not applicable to curved sheets. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Method of Carrying Out Transverse Test on Slates and Flat Sheets. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The purchaser, or his representative, for the purpose of carrying out the transverse test, may select six different slates or flat sheets from every batch of 10,000 slates or 1,000 flat sheets (or part thereof), from each of which shall be cut one square test specimen measuring 10 in. by 10 in.†, which shall be tested in the following manner : | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
†See note under the table in Clause 11. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
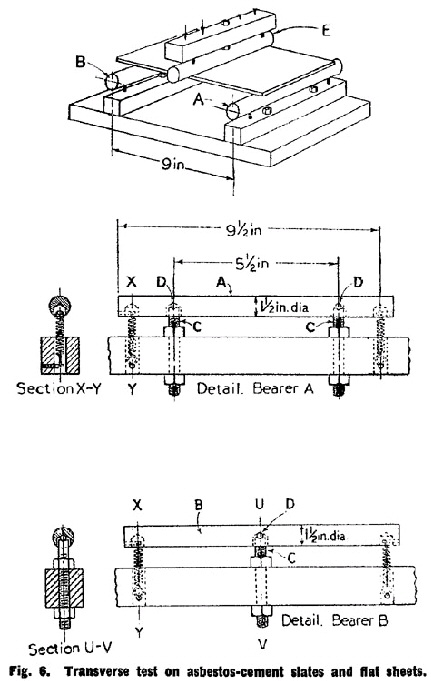
The specimen shall be completely immersed in water at a temperature of 58°F. (14·4°C.) to 64°F. (17·8°C.) for a period of 24 hours immediately prior to test. The test specimen is placed on self-aligning bearers A and B. Bearer A is supported horizontally on two bearer screws C which carry hardened steel balls D concentric with the bearer (see Fig. 6). Bearer B is supported on one such bearer screw and ball. The load is applied through bearer E, also having one bearer screw and ball. The bearers A, B and E are of mild steel not less than ¼ in. in diameter and each is provided with two springs which hold the bearers in position. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The distance between the bearers A and B at the points of contact with the test specimen is 9 in. Bearer E is midway between bearers A and B measured horizontally and rests upon the surface of the test specimen. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Bearers A and B are in the same horizontal plane, parallel to each other and to bearer E. The test specimen is placed centrally on bearers A and B. The load shall be applied at a uniform rate of 100 lb. per minute through the bearer E with a permissible variation of ± 10 per cent. in the rate. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
APPENDIX B. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Method of Carrying Out Transverse Test on Corrugated Sheets and Tiles. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The purchaser, or his representative, for the purpose of carrying out the transverse test, may select three corrugated sheets from every batch of 500 corrugated sheets (or part thereof), and each shall be tested in the following manner : | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
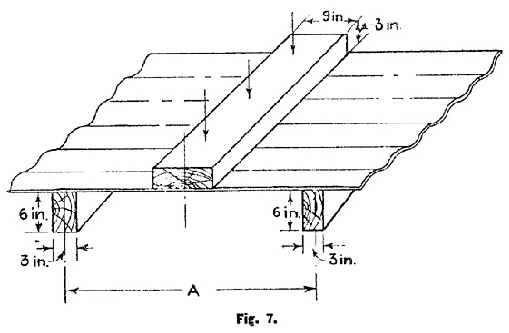
The sheet shall be completely immersed in water at a temperature of 58°F. (14·4°C.) to 64°F. (17·8°C.) for a period of 24 hours immediately prior to test. Each test specimen shall be free and evenly supported on parallel rigid hardwood bearers 3 in. wide and 6 in. deep and of a length at least as great as the width of the specimen and set at right angles to the corrugations as shown in Fig. 7. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For corrugated sheets of small section, the bearers shall be placed 2 ft. 6 in. from centre to centre (A). For corrugated sheets of large section and angular section the bearers shall be placed 3 ft. 6 in. from centre to centre (A). The load shall be applied along the centre line of the sheet through the 9 in. face of a 9 in. by 3 in, runner of the full width of the sheet upon the upper surface and parallel to the supports. The application of the load shall be at a uniform rate not greater than 400 lb. per minute. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
APPENDIX C. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Method of Carrying Out the Water Absorption Test. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The purchaser, or his representative, for the purpose of carrying out the water absorption test, may select three different slates or sheets from every batch of 10,000 slates, or 1,000 flat sheets or 500 corrugated sheets (or part thereof), from each of which shall be cut one test specimen measuring 7 in. x 3 in. The specimens shall be tested in the following manner : | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The test pieces shall be completely immersed in tap water at a temperature of 58°F. (14·4°C.) to 64°F. (17·8°C.) for a period of 18 hours. They shall be taken out, surplus moisture removed with a damp cloth, and weighed. They shall then be placed in a hot-air oven capable of being raised to 302°F. (150°C.) and maintained constant at that temperature. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Heating shall be commenced with the oven ventilator wide open, the temperature raised to 302°F. (150°C.) and maintained at this value for 4 hours. The test pieces shall then be removed, cooled for 1 to 2 hours in a desiccator and weighed at room temperature. The absorption is calculated as the difference in weight after immersion in water and heating as described above and expressed as a percentage of the weight after heating. The mean value of the specimens tested shall be taken. In carrying out the test not more than 30 specimens shall be placed in an oven of 1·8 cu. ft. internal capacity, or a proportionately greater number for a larger oven. The specimens shall not be placed in contact with one another, but shall be distributed uniformly throughout the oven. Wet specimens shall not be introduced into an oven in which the drying of other specimens is already in progress. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
APPENDIX D. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Method of Carrying Out Acid Solubility Test.* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
*This test is included to ensure that any cement used in the manufacture of asbestos-cement products has a resistance to acidic rain water and natural waters equal to that of Portland cement. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The purchaser, or his representative, for the purpose of carrying out the test for resistance to acidic waters, may select three different slates or sheets from every batch of 10,000 slates or 1,000 flat sheets or 500 corrugated sheets (or part thereof), from each of which shall be cut three test specimens, each measuring 6·5 cm. by 6·5 cm., giving a total surface area, including edges, of approximately 100 sq. cm. per specimen. The dimensions refer to the actual edge length whether the specimen is flat or curved. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Each test piece or pair of test pieces (see Note) shall be stood upright for 24 hours in 270 ml. of 5 per cent. acetic acid solution at a temperature of 58°F. (14·4°C.) to 64°F. (17·8°C.) contained in a vessel of such size that the specimen is entirely immersed. Separate vessels and solution shall be used for each test piece or pair of test pieces. The concentration of the acetic acid shall be determined, before and after immersion of the specimen, by titration against a solution of sodium hydroxide of known concentration (approximately 0·5N), using thymol blue as indicator. For the titration 10 ml. of the acid solution shall be taken, after first stirring the solution, diluted to 100 ml. and 10 drops of thymol blue solution (0·040 g. in 100 ml. 95 per cent. alcohol) added. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The end point to be taken is that at the colour change from yellow to blue corresponding to a pH change 8·0—9·5. The small amount of gelatinous precipitate formed does not interfere. The amount of acetic acid used per sq. cm. of area of the specimen is calculated as follows from the fall in concentration. Let x and y be the volumes in ml. of 0·5N Sodium Hydroxide (1 ml.=0·030 g. acetic acid) used at the initial and final titrations respectively. Let A be the area of unprotected asbestos-cement of the specimen in sq. cm. Then the weight in grammes of acetic acid used per sq. cm. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Note.—This test is a test of the asbestos-cement and not of any surface coating which may be applied to it. In the case of material provided with a protective or coloured surface coating, such coating shall be removed or protected. For materials coated on one side only the coated side shall be covered with a layer of paraffin wax applied hot and painted over the coating. Pairs of such specimens shall be placed in the test solution to maintain the exposed surface area at approximately 100 sq. cm. In the case of materials coated on both sides the coating shall be removed by abrasion from both sides and the specimen then tested as described in the above Appendix D. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTE. When so required, slates with chamfered corners as shown will be supplied. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
GIVEN under my Official Seal this 20th day of February, 1950. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DANIEL MORRISSEY, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Minister for Industry and Commerce. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||