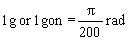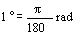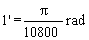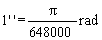S.I. No. 102/1976 - European Communities (Units of Measurement) Regulations, 1976.
S.I. No. 102 of 1976. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES (UNITS OF MEASUREMENT) REGULATIONS, 1976. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
I, JUSTIN KEATING, Minister for Industry and Commerce, in exercise of the powers conferred on me by Section 3 of the European Communities Act, 1972 (No. 27 of 1972) hereby make the following regulations: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1 Citation | 1. These regulations may be cited as the European Communities (Units of Measurement) Regulations: 1976. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2 Authorised units of measurement: metric system | 2. All units of measurement prescribed in Annex I, Chapter I (set out, as amended, in Schedule I of these regulations) of the Council Directive of the European Communities of 18 October, 1971 (71/ 354/EEC), as amended by the Act annexed to the Treaty of Accession of 22 January, 1972, are authorised for use in the State and all units of measurement in the metric system shall be determined in accordance with that Chapter. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
3 National metric standards | 3. The national standards for the metre (the unit of measurement of length) and the kilogram (the unit of measurement of mass) are described in Schedule II of these regulations and deposited in the Institute for Industrial Research and Standards. They shall be the standards by reference to which all other standards of those units and of any other unit of measurement derived wholly or partly from any of those units shall be maintained. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
4 Application | 4. These regulations apply to measuring instruments used, measurements made and dimensions or quantities expressed in units, whether for economic, public health, public safety or administrative purposes in the State. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5 Modification of legislation | 5. The provisions of the Weights and Measures Acts, 1878 to 1961, and any other relevant enactment shall be construed subject to these regulations and, in the event of any inconsistency between these regulations and any such provision, that provision shall, to the extent of the inconsistency, cease to have the force of law. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SCHEDULE I. * | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
AUTHORISED METRIC UNITS OF MEASUREMENT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1. SI UNITS AND THEIR DECIMAL MULTIPLES AND SUBMULTIPLES. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1.1 SI base units | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 SI base unit adopted by the International Committee of Weights and Measures (CIPM) on 7 October, 1969. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Definitions of SI base units: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unit of length: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The metre is the length equal to 1 650 763.73 wavelengths in vacuum of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the levels 2p10 and 5d5 of krypton-86 atom. (Eleventh CGPM (1960), Resolution 6). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unit of mass: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The kilogram is equal to the mass of the international prototype of the kilogram (Third CGPM (1901), p. 62 of the Conference Report). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unit of time: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The second is the duration of 9 192 631 770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium-133 atom. (Thirteenth CGPM (1967), Resolution 1). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unit of electric current: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The ampere is that constant current which, if maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible circular cross-section and placed 1 metre apart in a vacuum, would produce between these conductors a force equal to 2 x 10-7 newton per metre of length. (CIPM (1946), Resolution 2 approved by the Ninth CGPM (1948) ). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unit of thermodynamic temperature: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The kelvin is the fraction ½73.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water. (Thirteenth CGPM (1967), Resolution 4). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unit of luminous intensity: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The candela is the luminous intensity, in the perpendicular direction, of a surface of 1/600 000 square metre of a black body at the temperature of freezing platinum under a pressure of 101 325 newtons per square metre, (Thirteenth CGPM (1967), Resolution 5). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unit of amount of substance: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The mole is the amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kilogram of carbon-12. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
*Annex I, Chapter I, of Council Directive 71/354/EEC, as amended by Treaty of Accession, Annex I, X, 16. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTE: When the mole is used the elementary entities must be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other particles or specified groups of such particles. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1.1.1. Special name and symbol of the SI unit of temperature for expressing Celsius temperature | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Celsius temperature t is defined as the difference t = T-To between the two thermodynamic temperatures T and To where To = 273.15 K. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1.2. Other SI units | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1.2.1 Derived SI units | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Units derived coherently from SI base units are given as algebraic expressions in the form of power products of the SI base units with a numerical factor equal to 1. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1.2.2. SI units having special names and symbols | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1. Proposed by the CIPM for approval by the next CGPM. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2. Adopted by the 14th CGPM, 1971, Resolution No. 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Units derived from SI base units may be expressed in terms of the units listed in Chapters I and II, and of those listed in Chapter III of Council Directive 71/354/EEC as amended by the Treaty of Accession so long as these remain in use. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In particular, derived SI units may be expressed in terms of the special names and symbols in the above table. For example the SI unit of dynamic viscosity may be expressed as m-1. kg. s-1 or N. s/mor Pa.s. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The SI unit of power may be called volt-ampere (symbol 'VA') when it is used to express the apparent power of alternating electric current, and var (symbol 'var') when it is used to express reactive electric power. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1.3. Prefixes and their symbols used to designate certain decimal multiples and submultiples | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The names and symbols of the decimal multiples and submultiples of the unit of mass are formed by attaching prefixes to the word 'gram' and their symbols to the symbol 'g'. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Where a derived unit is expressed as a fraction, its decimal multiples and submultiples may be designated by attaching a prefix to units in the numerator or the denominator, or in both these parts. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Compound prefixes, that is to say prefixes formed by the juxtaposition of several of the above prefixes, may not be used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1.4. Special authorised names and symbols | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1.4.1. Special names and symbols of decimal multiples and submultiples of SI units. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1.4.2. Special names and symbols of decimal multiples and submultiples of SI units which may be used only in specialised fields. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1. The character * after a unit name or symbol indicates that these have not yet appeared in the lists drawn up by the CGPM or CIPM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTE: The prefixes listed in item 1.3 may be used in conjunction with the units contained in the tables of items 1.4.1 and 1.4.2. The multiple 102a is, however, called a 'hectare'. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2. UNITS WHICH ARE DEFINED ON THE BASIS OF SI UNITS BUT ARE NOT DECIMAL MULTIPLES OR SUBMULTIPLES THEREOF. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 No international symbol exists at present although there are national symbols and abbreviations, such as tr, ag. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2 The symbol g should disappear in favour of gon. The matter will be reviewed by 31 December, 1977. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTE: The prefixes listed in item 1.3 may only be used in conjunction with the names grade and gon and the symbols only with the symbol gon. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3. UNITS DEFINED INDEPENDENTLY OF THE SEVEN SI BASE UNITS. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The unified atomic mass unit is 1/12 of the mass of an atom of the nuclide 12C. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The electronvolt is the kinetic energy acquired by an electron passing in a vacuum from one point to another whose potential is 1 volt higher. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
*The value of these units, expressed in SI units, is not exactly known. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTE: The prefixes listed in item 1.3 may be used in conjunction with these two units. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4. UNITS AND NAMES OF UNITS PERMITTED IN SPECIALISED FIELDS ONLY. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOTE: The prefixes listed in item 1.3 may be used in conjunction with the above units. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5. COMPOUND UNITS. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Compound units are formed by combining the units of Chapters I, II and III of Council Directive No. 71/354/EEC as amended by the Treaty of Accession with the exception of those listed in items 1.4.2 and 4 of Chapter 1 and item 8.1 of Chapter III (units permitted in specialised fields only). The use of some of such compound units, where these are not derived SI units, will be examined by 31 December, 1977 with a view to deciding whether their use should be restricted or prohibited. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SCHEDULE II | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NATIONAL METRIC STANDARDS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Part I | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description of national standard of the metre | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Irish copy of the international metre being a bar about 1030 millimetres long, of simple H section, 24 millimetres wide by 24 millimetres high, made of 58% nickel steel having the upper face of web in neutral plane and a polished scale engraved thereon, bearing the inscription | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
An Méadan Naísiunta, Eire 1969 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The metre bar has also the following markings on the face: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
( a ) NI 58% No. 15481 20°C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
( b ) SIP Geneve Made in Switzerland | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
( c ) X NI 58% at its left extremity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
( d ) 5036 at its right extremity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Part 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description of national standard of the kilogram | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Irish copy of the international prototype of the kilogram being a mass of stainless steel "Immaculate V" (25% chrome, 20% nickel) in the form of a cylinder of revolution, of diameter approximately equal to its height, and has rounded edges. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
It is constructed of a single polished piece, without an interior cavity or attached pieces; on the upper face is placed the following identification mark: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
É | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 Kg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
69 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
GIVEN under my Official Seal, this 10th day of May, 1976. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
JUSTIN KEATING, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Minister for Industry and | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commerce. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
EXPLANATORY NOTE. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
These Regulations are made to give effect, so far as necessary, to Council Directive No. 71/354/EEC (as amended by the Treaty of Accession Annex 1, X, 16 and excluding Chapter II and III of Annex I and Annex II of the Directive) on the approximation of the laws of Member States relating to units of measurement. They authorise the SI system as the metric system for use in Ireland. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||